CIS vs. CCD comparison
CIS use a very small life-size magnification lens array to have sensor elements form an image and scan at the line level in close contact with the document. For this reason, the devices can be made smaller, thinner and lighter than CCDs that use regular lenses. Life-size magnification lens array have a shallow focus depth (limited working distance) and are not optimal for depth scanning, but they provide images without optical distortion. CIS scan in close contact, so there is little illumination leakage and less power consumption by the light source. Other features include single voltage operation and low power consumption because they use CMOS.
Life-size scanning (CIS method)
WHEC CIS can recognize invisible images by implementing various wavelengths to its light source.
In addition, by making the working distance longer, now WHEC CIS can scan a three-dimensional objects.
CIS(Contact Image Sensor)
Outline
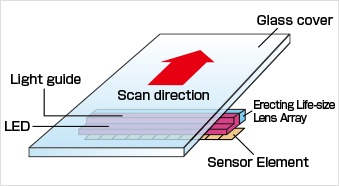
Reliable and high-speed authentication can be done by using visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light source.
Advantages
Small, thin and light-weight.
Wide-format scanning, such as A0 size is also easy.
No optical distortion due to life-size magnification scanning.
Low power consumption (due to single low voltage operation of CMOS sensor).
Low power consumption of light-source (contact scanning has less illumination leakage).
Disadvantages
Shallow focus depth (limited working distance).
Reduction scanning (CCD method)
Line Sensor
Outline
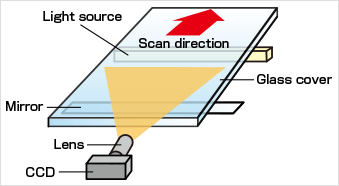
CCD scans the object at a distance by forming a reduced-size image on IC with reduction-lens and mirror.
Advantages
Deep Focal range (long working distance).
Narrow width can be scanned at ultra-high resolution (however,reduction-lens is expensive).
Disadvantages
Limitation on downsizing because of the necessity of reduction optical path.
Optical distortion occurs at the reduction-lens.
Divided/splitted scanning might be required for a wide scanning width to avoid the optical distortion of the reduction-lens. In this case, multiple sensor units (lens + CCD) are necessary.
CCD element requires high power consumption due to its multiple drive power supplies.
Mechanical alignment is required.
Area Sensor
Outline
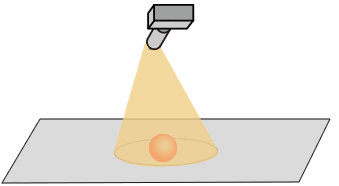
Image capture using area sensor.
Advantages
Deep Focal range (long working distance).
Narrow width can be scanned at ultra-high resolution (however,reduction-lens is expensive).
Because of its long working-distance, three-dimensional objects can be easily scanned (area sensor).
Disadvantages
Limitation on downsizing because of the necessity of reduction optical path.
Optical distortion occurs at the reduction-lens.
Divided/splitted scanning might be required for a wide scanning width to avoid the optical distortion of the reduction-lens. In this case, multiple sensor units (lens + CCD) are necessary.
CCD element requires high power consumption due to its multiple drive power supplies.
Mechanical alignment is required.
Want to know more about CIS?
CIS Application Scenarios | WHEC (w-hec.com)
CIS Application Battery Film Inspection | WHEC (w-hec.com)
CIS Application Printing Inspection | WHEC (w-hec.com)
New CIS technology for strong-reflective surface inspection | WHEC (w-hec.com)
